How to use Kari?
Kari is best used as a place to dump temporary/non-serious information. It doesn’t aim to replace other note-taking apps. It shines the best when you want a scratchpad to offload random information/thoughts and do some quick back-of-the-envelope calculations.
Keyboard Shortcuts
| Action | Shortcuts |
|---|---|
| Create new block | ⌘ + return |
| Create markdown block | ⌘ + 1 |
| Create JavaScript block | ⌘ + 2 |
| Create math block | ⌘ + 3 |
| Create json block | ⌘ + 4 |
Create new block
When you hit ⌘ + return, Kari will create a new block in the current scratchpad using the last block type that was used. Otherwise, it will create a markdown block.
Calendar
When you forget which scratchpad you’ve put a piece of information into, you can use the calendar view to filter out the blocks that been created/changed on a specific date. Days with blue dots indicate that it contains notes that’s been changed or created. Simply click on a day to filter the blocks that was changed on that day.
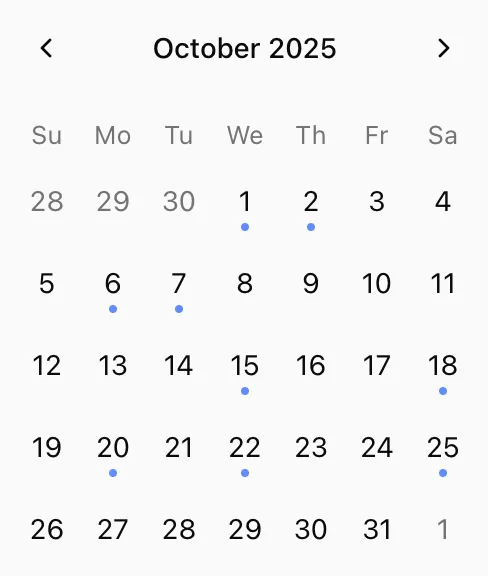
You can turn off calendar feature in settings.
Math Syntax
Unit Conversion
Kari support a few basic unit conversions such as:
- Length (cm to m, m to km, etc.)
- Degree (and radian)
- and more.
You can use the keyword to to perform the conversion:
10cm to m
20m to cmOperators
Basic maths operators are supported:
| Operator | Symbols |
|---|---|
| Addition | +, plus |
| Subtraction | -, minus |
| Multiplication | *, times |
| Division | /, divide |
| Modulo | % |
10cm + 2m = 210cm
$100 * 3 people = $300
$20 times 3 = $60Percentage
You can also use the operator of when dealing percentage:
20% of 10 = 2Numbers
Number by default are base 10, but you can also write binary or hexadecimal using the correct prefix
0b00010 = 2 in binary
0x29 = 41 in hexadecimal
0o51 = 41 in octalArray
You can group a list of values together into an array using brackets:
arr = [1, 2.2, pi, e]Then you can use array functions like sum to interact with it:
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]
sum(arr) = 10Variables
Any value can be assigned to a variable using the = operator. Variable name
cannot contains whitespace.
age = 10
in_five_years = age + 5Constants
pi = 3.1415926535898
e = 2.718281828459Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| abs(x) | Calculate the absolute value of a number |
| ceil(x) | Round a value towards plus infinity If x is complex, both real and imaginary part are rounded towards plus infinity. |
| floor(x) | Round a value towards minus infinity. |
| cube(x) | Compute the cube of a value, x * x * x. |
| square(x) | Compute the square of a value, x * x. |
| pow(x, y) | Calculates the power of x to y, x ^ y. |
| sqrt(x) | Calculate the square root of a value. |
| log(x, base) | Calculate the logarithm of a value. Default base is e |
| hypot(a, b, c, …) | Calculate the hypotenuse of a list with values. The hypotenuse is defined as: sqrt(a^2 + b^2 + c^2 + …) |
Previous Result
In Kari, the keyword that is reserved to store the value of previous
expression. For example:
10 + 10 = 20
that = 20
$10 times 3 people = $30.00
that - 15% = $25.50Money (feature in progress)
By default, Kari interpret $<number> as money and will use USD as the
default currency if no currency is specified. However, currently converting money isn’t supported.
$30 = 30.00 USDTo provide currency, you can write the amount followed by the short code of the currency (uppercase or lowercase is allowed):
5 usd = 5.00 USD
2 aud = 2.00 AUD